Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Evaluate source characterization performance.¶
This example demonstrates how to evaluate the performance of a beamforming algorithm using
the acoular.tools.metrics.MetricEvaluator class to calculate the metrics introduced in
[1].
from pathlib import Path
import acoular as ac
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from acoular.tools import MetricEvaluator
Set up the parameters
sfreq = 51200
duration = 1
num_samples = duration * sfreq
micgeofile = Path(ac.__file__).parent / 'xml' / 'array_64.xml'
Generate test data, in real life this would come from an array measurement
mg = ac.MicGeom(file=micgeofile)
n1 = ac.WNoiseGenerator(sample_freq=sfreq, num_samples=num_samples, seed=1)
n2 = ac.WNoiseGenerator(sample_freq=sfreq, num_samples=num_samples, seed=2, rms=0.7)
n3 = ac.WNoiseGenerator(sample_freq=sfreq, num_samples=num_samples, seed=3, rms=0.5)
p1 = ac.PointSource(signal=n1, mics=mg, loc=(-0.1, -0.1, -0.3))
p2 = ac.PointSource(signal=n2, mics=mg, loc=(0.15, 0, -0.3))
p3 = ac.PointSource(signal=n3, mics=mg, loc=(0, 0.1, -0.3))
pa = ac.Mixer(source=p1, sources=[p2, p3])
Analyze the data and generate a deconvolved source map with CLEAN-SC
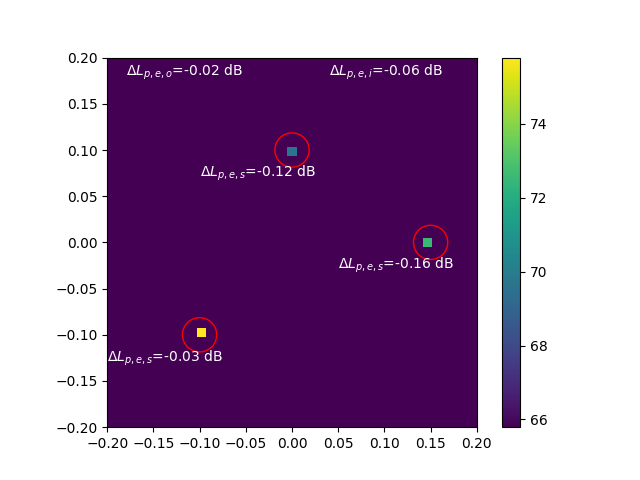
Evaluate the results: Therefore, we define a custom grid containing the source locations.
Next, we define the target squared sound pressure values for each source.
Finally, we use the acoular.tools.metrics.MetricEvaluator class to evaluate the
reconstruction accuracy of the beamforming algorithm with three different metrics. A circular
sector with a radius of 5% of the aperture is used to define the sectors for the evaluation.
mv = MetricEvaluator(
sector=ac.CircSector(r=0.05 * mg.aperture),
grid=rg,
data=pm.reshape((1, -1)),
target_grid=target_grid,
target_data=target_data,
)
Plot the data
plt.figure()
# show map
plt.imshow(Lm.T, origin='lower', vmin=Lm.max() - 10, extent=rg.extend(), interpolation='none')
# plot sectors
ax = plt.gca()
for j, sector in enumerate(mv.sectors):
ax.add_patch(plt.Circle((sector.x, sector.y), sector.r, color='red', fill=False))
# annotate specific level error below circles
plt.annotate(
r'$\Delta L_{p,e,s}$=' + str(round(mv.get_specific_level_error()[0, j], 2)) + ' dB',
xy=(sector.x - 0.1, sector.y - sector.r - 0.01),
color='white',
)
# annotate overall level error
plt.annotate(
r'$\Delta L_{p,e,o}$=' + str(round(mv.get_overall_level_error()[0], 2)) + ' dB',
xy=(0.05, 0.95),
xycoords='axes fraction',
color='white',
)
plt.annotate(
r'$\Delta L_{p,e,i}$=' + str(round(mv.get_inverse_level_error()[0], 2)) + ' dB',
xy=(0.6, 0.95),
xycoords='axes fraction',
color='white',
)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.346 seconds)
